European Qualifications Framework (EQF)
The IEQAB follows EQF Qualifications Framework while evaluation credentials and issues or awards IEQAB Diploma. The EU developed the European Qualifications Framework (EQF) as a translation tool to make national qualifications easier to understand and more comparable. The EQF seeks to support cross-border mobility of learners and workers, promote lifelong learning and professional development across Europe.
What is the EQF?
The EQF is an 8-level, learning outcomes-based framework for all types of qualifications that serves as a translation tool between different national qualifications frameworks. This framework helps improve transparency, comparability and portability of people’s qualifications and makes it possible to compare qualifications from different countries and institutions.
Which countries are involved with EQF?
In addition to the EU Member States another 11 countries work towards implementing the EQF, namely Iceland, Liechtenstein and Norway (European Economic Area countries), Albania, North Macedonia, Montenegro, Serbia and Türkiye (candidate countries), Bosnia & Herzegovina, Kosovo ** (potential candidates) and Switzerland.
Description of the eight EQF levels
Each of the 8 levels of the EQF is defined by a set of descriptors indicating the learning outcomes relevant to qualifications at that level in any qualifications system.
The learning outcomes are defined in terms of:
Knowledge: in the context of EQF, knowledge is described as theoretical and/or factual.
Skills: In the context of EQF, skills are described as cognitive (involving the use of logical, intuitive and creative thinking) and practical (involving manual dexterity and the use of methods, materials, tools and instruments).
Responsibility and autonomy: In the context of the EQF responsibility and autonomy is described as the ability of the learner to apply knowledge and skills autonomously and with responsibility.
Level 1 – Learning Outcomes:
Knowledge Skills Responsibility and autonomy
| Basic general knowledge | Basic skills required to carry out simple tasks | Work or study under direct supervision in a structured context |
Level 2 – Learning Outcomes:
Knowledge Skills Responsibility and autonomy
| Basic factual knowledge of a field of work or study | Basic cognitive and practical skills required to use relevant information in order to carry out tasks and to solve routine problems using simple rules and tools | Work or study under supervision with some autonomy |
Level 3 – Learning Outcomes:
Knowledge Skills Responsibility and autonomy
| Knowledge of facts, principles, processes and general concepts, in a field of work or study | A range of cognitive and practical skills required to accomplish tasks and solve problems by selecting and applying basic methods, tools, materials and information | Take responsibility for completion of tasks in work or study; adapt own behaviour to circumstances in solving problems |
Level 4 – Learning Outcomes:
Knowledge Skills Responsibility and autonomy
| Factual and theoretical knowledge in broad contexts within a field of work or study | A range of cognitive and practical skills required to generate solutions to specific problems in a field of work or study | Exercise self-management within the guidelines of work or study contexts that are usually predictable, but are subject to change; supervise the routine work of others, taking some responsibility for the evaluation and improvement of work or study activities |
Level 5 – Learning Outcomes:
Knowledge Skills Responsibility and autonomy
| Comprehensive, specialised, factual and theoretical knowledge within a field of work or study and an awareness of the boundaries of that knowledge | A comprehensive range of cognitive and practical skills required to develop creative solutions to abstract problems | Exercise management and supervision in contexts of work or study activities where there is unpredictable change; review and develop performance of self and others |
Level 6 – Learning Outcomes:
Knowledge Skills Responsibility and autonomy
| Advanced knowledge of a field of work or study, involving a critical understanding of theories and principles | Advanced skills, demonstrating mastery and innovation, required to solve complex and unpredictable problems in a specialised field of work or study | Manage complex technical or professional activities or projects, taking responsibility for decision-making in unpredictable work or study contexts; take responsibility for managing professional development of individuals and groups |
Level 7 – Learning Outcomes:
Knowledge Skills Responsibility and autonomy
| Highly specialised knowledge, some of which is at the forefront of knowledge in a field of work or study, as the basis for original thinking and/or research
Critical awareness of knowledge issues in a field and at the interface between different fields |
Specialised problem-solving skills required in research and/or innovation in order to develop new knowledge and procedures and to integrate knowledge from different fields | Manage and transform work or study contexts that are complex, unpredictable and require new strategic approaches; take responsibility for contributing to professional knowledge and practice and/or for reviewing the strategic performance of teams |
Level 8 – Learning Outcomes:
Knowledge Skills Responsibility and autonomy
| Knowledge at the most advanced frontier of a field of work or study and at the interface between fields | The most advanced and specialised skills and techniques, including synthesis and evaluation, required to solve critical problems in research and/or innovation and to extend and redefine existing knowledge or professional practice | Demonstrate substantial authority, innovation, autonomy, scholarly and professional integrity and sustained commitment to the development of new ideas or processes at the forefront of work or study contexts including research |
For More details regarding EQF Link: https://europass.europa.eu/en/europass-digital-tools/european-qualifications-framework
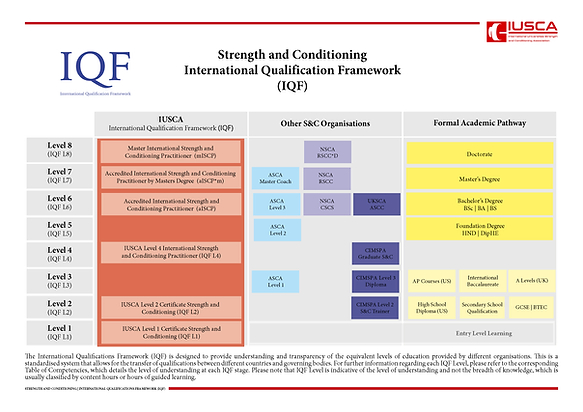
International Qualifications Framework (IQF)
IEQAB also follows and recognises IQF (International Qualifications Framework). According to the cedefop.europa.eu :
- International qualifications frameworks are set up to respond to the increasing mobility of learners and workers, and to the need for describing, comparing and recognising qualifications developed at national, international or sectoral level;
- within the EU, the eight levels of the European qualifications framework for lifelong learning (EQF) cover the entire span of qualifications from those recognising basic knowledge, skills and competences to those awarded at the highest level of academic, professional and vocational education and training.
For more information regarding IQF, Link: https://www.cedefop.europa.eu/en/tools/vet-glossary/glossary/internationaler-qualifikationsrahmen#:~:text=Instrument%20for%20developing%2C%20classifying%20and,specified%20levels%20of%20learning%20outcomes.
IEQAB is a Subscribing Member of IUSCA, Leeds, England for the Global Community:
International Universities Strength and Conditioning Association (IUSCA)
Developed following the landmark academic paper published by the International Universities Strength and Conditioning Association, The IQF uses a standardized rating system, modelled after the European Qualifications Framework (EQF) and Regulated Qualifications Framework (RQF), which categorizes qualifications into levels from 1 to 8.
Structure of the IQF
Developed following the landmark academic paper published by the International Universities Strength and Conditioning Association, The IQF uses a standardized rating system, modelled after the European Qualifications Framework (EQF) and Regulated Qualifications Framework (RQF), which categorizes qualifications into levels from 1 to 8.
These levels correspond to different stages of education and professional development:
-
Level 1: Foundational learning, equivalent to early school education.
-
Level 2: Basic knowledge and skills, comparable to high school education.
-
Level 3: Intermediate knowledge, suitable for further education or entry-level work.
-
Level 4 to 6: Advanced learning and professional skills, including undergraduate degrees.
-
Level 7: Specialized knowledge for expert professional practice, equivalent to a master’s degree.
-
Level 8: Highest level of academic and professional achievement, equivalent to a doctoral degree.
Source: International Qualification Framework | IUSCA
IEQAB also follows and recognises ICDL Foundation Qualification Frameworks Worldwide:
ICDL Foundation supports the initiatives of National Operators in Europe, Americas and the Middle East and North African (MENA) territories from her headquarters in Dublin, Ireland and her ICDL Europe office in Brussels, Belgium. ICDL have also established two regional operations – ICDL Africa (based in Rwanda) and ICDL Asia (based in Singapore). All ICDL operations work closely with regional, national and local partners to develop the global network of ICDL Accredited Test Centres.
ICDL and qualification frameworks worldwide
Qualifications frameworks, like the European Qualifications Framework, make it easy to compare qualifications and certifications from different countries with each other. International qualifications, such as ICDL, can be mapped to National Qualification Frameworks (NQFs) and, in this way, become officially recognised in different countries in Europe and worldwide. The ICDL programme has been mapped to NQFs in a number of countries.
ICDL Foundation has produced a brochure to overview qualifications frameworks around the world, and to explain how the ICDL programme fits into them. ICDL Qualification Frameworks Brochure may be viewed here: ICDL EQF-Brochure_final_web
For more information regarding ICDL , Link: https://icdl.org/policy-and-publications/icdl-and-qualification-frameworks-worldwide/